
Development of web-applications with the help of Spring MVC implies creation of several logical layers of architecture. One of the layers is a DAO (Repository) layer. It is responsible for communication with a database. If you developed the DAO layer at least once, you should know that it involves a lot of boilerplate code. A Spring Data take a part of the routine job related to the DAO on itself.
In the post I’m going to provide an example of application which will demonstrateSpring Data (JPA) in conjunction with Spring MVC, MySQL and Maven.Hibernate will be used as implementation of the JPA. As you probably know, I’m a real fan of java based configurations, so I will use this approach to configure the Spring Data. In the end of the tutorial you can find a link to the sample project on GitHub.
Preparation
In the article I want to concentrate on the Spring Data, so all stuff which is out topic I will omit. But in the start I want provide a bulk of links which can be helpful for you in context of this tutorial.
- Creation of dynamic web project in Eclipse with Maven.
- Simple Spring MVC application with the java based configuration.
- Spring MVC + Hibernate sample application.
These links should give answers on 90% of questions which can occur during reading the post. Let’s start with table creation in the MySQL:
- CREATE TABLE `shops` (
- `id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
- `name` varchar(60) NOT NULL,
- `employees_number` int(6) NOT NULL,
- PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
- ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Now we can go ahead with a java code:
- @Entity
- @Table(name = “shops”)
- public class Shop {
- @Id
- @GeneratedValue
- private Integer id;
- private String name;
- @Column(name = “employees_number”)
- private Integer emplNumber;
- public Integer getId() {
- return id;
- }
- public void setId(Integer id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public Integer getEmplNumber() {
- return emplNumber;
- }
- public void setEmplNumber(Integer emplNumber) {
- this.emplNumber = emplNumber;
- }
- }
Configuration of Spring Data
I believe that a screenshot of the project will help you to understand what’s going on.
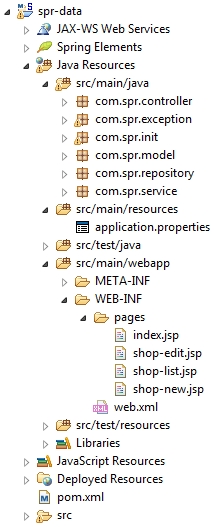
In the property file concentrated all configuration data:
- #DB properties:
- db.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibnatedb
- db.username=hibuser
- db.password=root
- #Hibernate Configuration:
- hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
- hibernate.show_sql=true
- entitymanager.packages.to.scan=com.spr.model
The WebAppConfig class contains all java based configurations:
- @Configuration
- @EnableWebMvc
- @EnableTransactionManagement
- @ComponentScan(“com.spr”)
- @PropertySource(“classpath:application.properties”)
- @EnableJpaRepositories(“com.spr.repository”)
- public class WebAppConfig {
- private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_DATABASE_DRIVER = “db.driver”;
- private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_DATABASE_PASSWORD = “db.password”;
- private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_DATABASE_URL = “db.url”;
- private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_DATABASE_USERNAME = “db.username”;
- private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_DIALECT = “hibernate.dialect”;
- private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_SHOW_SQL = “hibernate.show_sql”;
- private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_ENTITYMANAGER_PACKAGES_TO_SCAN = “entitymanager.packages.to.scan”;
- @Resource
- private Environment env;
- @Bean
- public DataSource dataSource() {
- DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
- dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getRequiredProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_DATABASE_DRIVER));
- dataSource.setUrl(env.getRequiredProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_DATABASE_URL));
- dataSource.setUsername(env.getRequiredProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_DATABASE_USERNAME));
- dataSource.setPassword(env.getRequiredProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_DATABASE_PASSWORD));
- return dataSource;
- }
- @Bean
- public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory() {
- LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactoryBean = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
- entityManagerFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource());
- entityManagerFactoryBean.setPersistenceProviderClass(HibernatePersistence.class);
- entityManagerFactoryBean.setPackagesToScan(env.getRequiredProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_ENTITYMANAGER_PACKAGES_TO_SCAN));
- entityManagerFactoryBean.setJpaProperties(hibProperties());
- return entityManagerFactoryBean;
- }
- private Properties hibProperties() {
- Properties properties = new Properties();
- properties.put(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_DIALECT, env.getRequiredProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_DIALECT));
- properties.put(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_SHOW_SQL, env.getRequiredProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_HIBERNATE_SHOW_SQL));
- return properties;
- }
- @Bean
- public JpaTransactionManager transactionManager() {
- JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
- transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(entityManagerFactory().getObject());
- return transactionManager;
- }
- @Bean
- public UrlBasedViewResolver setupViewResolver() {
- UrlBasedViewResolver resolver = new UrlBasedViewResolver();
- resolver.setPrefix(“/WEB-INF/pages/”);
- resolver.setSuffix(“.jsp”);
- resolver.setViewClass(JstlView.class);
- return resolver;
- }
- }
Pay your attention at @EnableJpaRepositories annotation. It enables usage of JPA repositories. The com.spr.repository package will be scaned to detect repositories. In the entityManagerFactory bean I determined that Hibernate will be used as JPA implementation.
Initializer class will be omitted.
DAO & Service layers
The repository for the Shop entity:
- package com.spr.repository;
- import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
- import com.spr.model.Shop;
- public interface ShopRepository extends JpaRepository<shop, integer=“”> {
- }
- </shop,>
Definitely it is the most simplest code snippet in the tutorial. But it requires the most high attention. The JpaRepository interface contains the basic operations which can be performed with any entity (CRUD operations). More information you can find on the official documentation page.
Here is a code of the ShopService interface:
- public interface ShopService {
- public Shop create(Shop shop);
- public Shop delete(int id) throws ShopNotFound;
- public List<shop> findAll();
- public Shop update(Shop shop) throws ShopNotFound;
- public Shop findById(int id);
- }
- </shop>
And the implementation of the service interface:
- import java.util.List;
- import javax.annotation.Resource;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
- import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
- import com.spr.exception.ShopNotFound;
- import com.spr.model.Shop;
- import com.spr.repository.ShopRepository;
- @Service
- public class ShopServiceImpl implements ShopService {
- @Resource
- private ShopRepository shopRepository;
- @Override
- @Transactional
- public Shop create(Shop shop) {
- Shop createdShop = shop;
- return shopRepository.save(createdShop);
- }
- @Override
- @Transactional
- public Shop findById(int id) {
- return shopRepository.findOne(id);
- }
- @Override
- @Transactional(rollbackFor=ShopNotFound.class)
- public Shop delete(int id) throws ShopNotFound {
- Shop deletedShop = shopRepository.findOne(id);
- if (deletedShop == null)
- throw new ShopNotFound();
- shopRepository.delete(deletedShop);
- return deletedShop;
- }
- @Override
- @Transactional
- public List<shop> findAll() {
- return shopRepository.findAll();
- }
- @Override
- @Transactional(rollbackFor=ShopNotFound.class)
- public Shop update(Shop shop) throws ShopNotFound {
- Shop updatedShop = shopRepository.findOne(shop.getId());
- if (updatedShop == null)
- throw new ShopNotFound();
- updatedShop.setName(shop.getName());
- updatedShop.setEmplNumber(shop.getEmplNumber());
- return updatedShop;
- }
- }
- </shop>
In this way the ShopRepository is used.
Controller
Finally I can use ShopSrviceImpl class in the controller. All JSP pages will be omitted, so you can find them source code on the GitHub.
- @Controller
- @RequestMapping(value=“/shop”)
- public class ShopController {
- @Autowired
- private ShopService shopService;
- @RequestMapping(value=“/create”, method=RequestMethod.GET)
- public ModelAndView newShopPage() {
- ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(“shop-new”, “shop”, new Shop());
- return mav;
- }
- @RequestMapping(value=“/create”, method=RequestMethod.POST)
- public ModelAndView createNewShop(@ModelAttribute Shop shop,
- final RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
- ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView();
- String message = “New shop “+shop.getName()+” was successfully created.”;
- shopService.create(shop);
- mav.setViewName(“redirect:/index.html”);
- redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute(“message”, message);
- return mav;
- }
- @RequestMapping(value=“/list”, method=RequestMethod.GET)
- public ModelAndView shopListPage() {
- ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(“shop-list”);
- List<shop> shopList = shopService.findAll();
- mav.addObject(“shopList”, shopList);
- return mav;
- }
- @RequestMapping(value=“/edit/{id}”, method=RequestMethod.GET)
- public ModelAndView editShopPage(@PathVariable Integer id) {
- ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(“shop-edit”);
- Shop shop = shopService.findById(id);
- mav.addObject(“shop”, shop);
- return mav;
- }
- @RequestMapping(value=“/edit/{id}”, method=RequestMethod.POST)
- public ModelAndView editShop(@ModelAttribute Shop shop,
- @PathVariable Integer id,
- final RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) throws ShopNotFound {
- ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(“redirect:/index.html”);
- String message = “Shop was successfully updated.”;
- shopService.update(shop);
- redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute(“message”, message);
- return mav;
- }
- @RequestMapping(value=“/delete/{id}”, method=RequestMethod.GET)
- public ModelAndView deleteShop(@PathVariable Integer id,
- final RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) throws ShopNotFound {
- ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(“redirect:/index.html”);
- Shop shop = shopService.delete(id);
- String message = “The shop “+shop.getName()+” was successfully deleted.”;
- redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute(“message”, message);
- return mav;
- }
- }
- </shop>
Summary
The Spring Data is very powerful weapon, it helps you develop an application more faster and avoid hundreds of boilerplate strings of code. Usage of Spring Data is the most convenient way to create a DAO layer in an application, so don’t ignore it in your projects.
